NEW DELHI, India — As a woman in my twenties who grew up in India — a country where abuse of women has been described as the biggest human rights violation on Earth — the SlutWalks of 2011 were, frankly, bewildering.
Every day of our lives, women like me were taught to go over a mental checklist of ways to avoid getting raped. The list had become second nature, so deeply, seamlessly internalized that the doorbell only had to ring, and my mother and I, hanging out in our home, watching TV, or maybe making dinner, would first reach for a scarf to throw over our bodies before we answered the door. At my high school, where uniforms were mandatory, girls were asked to kneel on the ground, so the teachers could check if our skirts were long enough. If they didn’t touch the ground, they were too short, and a particularly terrifying teacher would rip open the hem of our skirts, those frayed edges marking us for the rest of the school day. There were a million ways to dress like a slut if you were a girl (there were no such codes for boys) — our white shirts could be “too transparent” if the cotton had worn thin from frequent washing or if we wore colored bras inside instead of white or “skin”-colored ones.
When I was a 25-year-old reporter, I went to ask a group of young girls who lived in a slum in Govandi, Mumbai, what their checklist looked like. What did paranoia look like in a place where thin corrugated sheets of steel were all that stood between the girls and their neighbors, adult men, leering boys?
Fourteen-year-old Nafisa told me she made sure she texted her friend Neelu before she left home. Neelu carried red chili powder with her everywhere she went in case she needed to throw it in the eyes of a potential attacker. Annu made sure her water bottle was always full so that she had something heavy to hit a potential molester with. Pinki had stopped wearing glass bangles once she turned 11 — because her mother told her that if someone grabbed her wrists, they would break and injure her, slowing her down as she ran from her attackers. Neena had stopped wearing her hair down because it attracted too much attention. At 15, most of them avoided going outdoors unless it was absolutely necessary, and when they did, they were usually accompanied by an older male from the family. A lot of the older girls carried small knives in their bags but were unsure if they’d be able to use them when the time came.
Some girls who wore hijabs said they did not feel any safer: “They want to find out what is underneath,” Nafisa said.
If adulthood was the steady accumulation of survival skills — a realization of one’s own power and its limitations — womanhood, for as long as I’d known it, appeared to be about developing a sixth sense that warned you when you were in a specific kind of danger from a man. But the news we read every day, of women abducted, burnt, raped, killed, appeared to be filled with women whose sixth sense had let them down.

The comment that sparked the first SlutWalk, leading to gatherings across 200 cities and 40 countries, didn’t even seem particularly surprising to me. A police officer in Toronto had said to a group of students: “I’ve been told I’m not supposed to say this, however, women should avoid dressing like sluts in order not to be victimized.” It was the kind of thing that ministers, judges, police officers, holy men, and celebrities constantly repeated across the world.
But as the protests began to go viral, we dissected the SlutWalks avidly, over Facebook posts and IRL, in quiet, thrilled tones with other women. When Indian women held their own version of the SlutWalk — the Besharmi Morcha, or the March of Shamelessness — we cheered them on. But privately, I wondered if the entire project of reclaiming a pejorative word was counterintuitive. Did we really need to normalize the word “slut,” or the behavior associated with it, when there was so much else at stake — especially in a country where women struggled for basic rights?
And then there was the question of inclusivity, posed in the open letter from black women to SlutWalk organizers: Who can afford to reclaim the word “slut”? Who are the women whose bodies are always already considered sexualized and without agency by the patriarchy, and did the marches have space for sex workers? Trans women? Dalit women? Were the SlutWalks about provocation or about language? Were they only for the rights of privileged white women? Could we ever change the power imbalance that routinely blamed women for inviting sexual assault just by walking down a street?
In 2012, the conversation turned dark and urgent in India, when the gang rape and murder of a young woman in New Delhi sent tens of thousands of women marching on the streets. Overnight, our fear had birthed an inchoate rage — against the culture of shame, against the constant policing of our bodies and clothes and words and movement. We wanted more than just the right to be safe, we wanted the right to roam the streets and hang out in public and take risks and have fun like any man, without fear of assault. We demanded justice; we also demanded joy. And for a moment, it seemed as though something might really change.
The next year, the world changed so much that it became unrecognizable to me. I was sexually assaulted, not by a stranger on a dark street corner, but by a person I had known and trusted for many years. I testified in court against him and felt as though I had set my entire life on fire. I lost my job, moved cities, moved back in with my mother. Scores of people and professional opportunities disappeared from my life. (The accused denies any wrongdoing.)
From the depths of my nightmare, SlutWalk, even with its problems, represented a spectacle of sex-positivity. It felt like a world of color and hope that I would never inhabit again. People from a range of genders and ages were still gathering in Spain, South Africa, India, and Pakistan, marching in the streets wearing school uniforms, office clothes, lace and leather, nuns’ habits, fishnets, and denim — flashing skin, drumming, dancing, holding babies and signs, and sharing stories of rape and assault and trauma and songs and jokes.
Meanwhile, I was called a slut all the time, by people close to the man who abused me, his lawyers, others who had never met me but were convinced I had lied — by strangers on the internet. I became less interested in reclaiming words and dissecting them. I was tired and suicidal, and I wanted to focus on being something more than, other than, separate from what happened to me and my body. The SlutWalks were described as the most successful feminist action of the last two decades. What good was any of it going to do?
It wasn’t until 2017, when women first began to speak publicly and loudly about Harvey Weinstein and the things they said he had done, that the fog of the past few years started to clear: For some of us, the SlutWalks had been our first moment of articulating collective rage.
For women, particularly those who were in our twenties or younger when this decade began, our only point of reference for women’s rage had been photographs from the anti-rape movements of the ’60s and ’70s, or marches called “Take Back the Night” — women occupying city streets at hours when decent women were supposed to be safe at home. Some of us knew about feminist theory, the first wave and the second and the third, still more of us knew that no matter where we were, our rights were precarious. Many of us now had opportunities our grandmothers could only dream of, but we were marching for the same old shit. Our bodies were still our first battlegrounds.

The next billion people — including women — who are learning about the power of collective action on the internet are from places like India, China, South Africa, Brazil, and the Middle East. These women have grown up in worlds where public spaces are fraught with danger and private spaces are frequently regarded with shame. As a teenage girl in Pakistan learns a new language of sexual freedom and identity online, she is also learning to navigate the murky waters of digital abuse that a woman lawmaker in the US is punished for. The cautionary tales of trolling, doxing, being targeted with rape threats, having intimate photographs posted online for all to gawk at, being morphed onto naked bodies on a random porn site all exist. But so do the possibilities of forming solidarities, joining protests beyond geographical confines, allowing more women than ever before to have a voice — and to listen in. The measure of successful feminist action, I learned this decade, has never been only about changing laws, governments, or workplace policies. Anger itself is clarifying, because it changes us, the people who participate in it, by giving us ways of seeing: seeing ourselves as part of a collective, seeing through patterns of abuse, seeing as in witnessing each other’s lives and stories.
In this decade, we have seen women’s rage move front and center — it is the subject of books and films and television shows. Beyoncé feels it, so does Greta Thunberg — a 16-year-old climate activist who only recently was told by the president of the US to seek anger management.
But, in workplaces, in courtrooms, at universities, on red carpets and during election campaigns, women are still expected to articulate that anger in the most bloodless way possible, in order to seem rational, likable, electable, and believable.
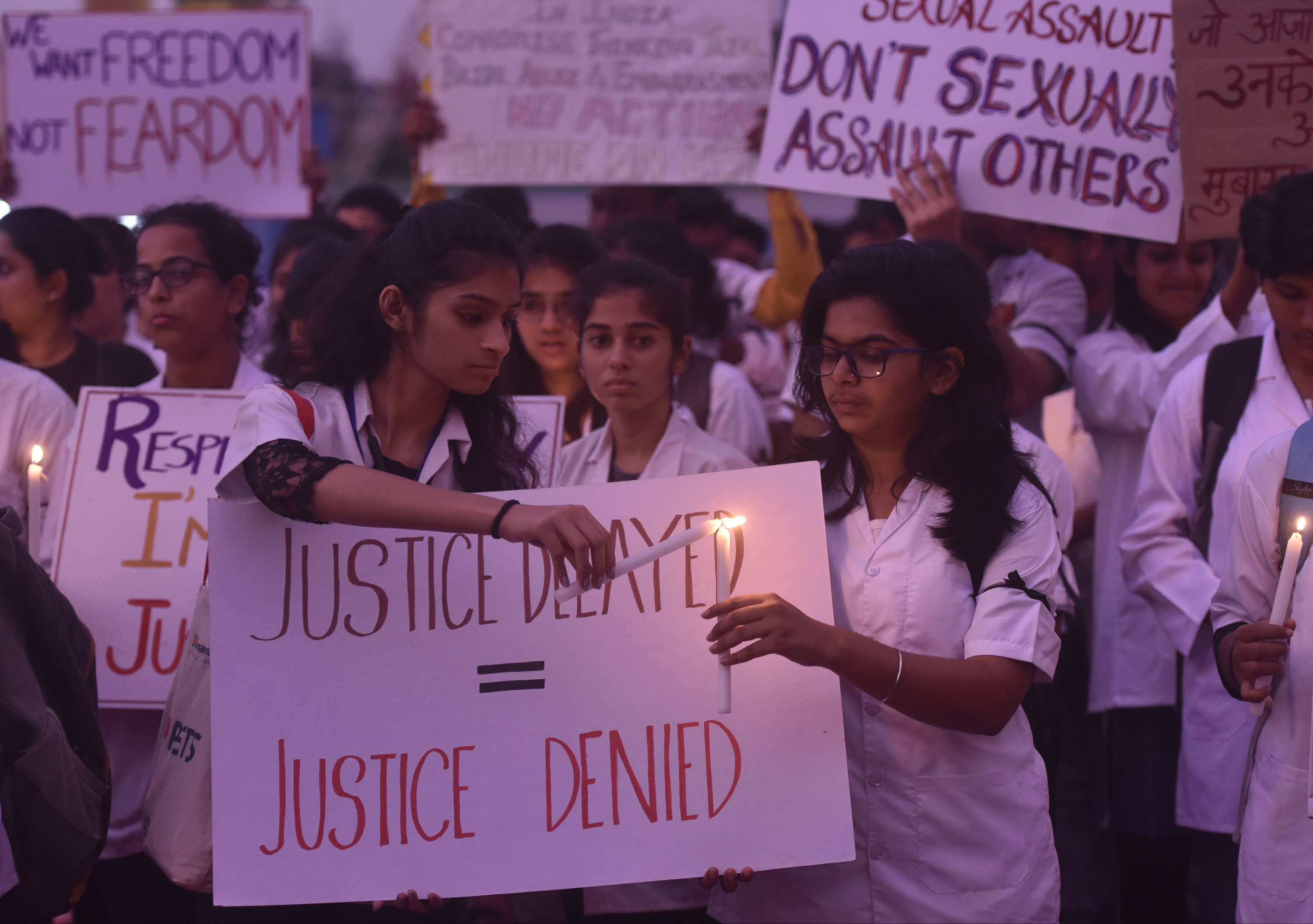
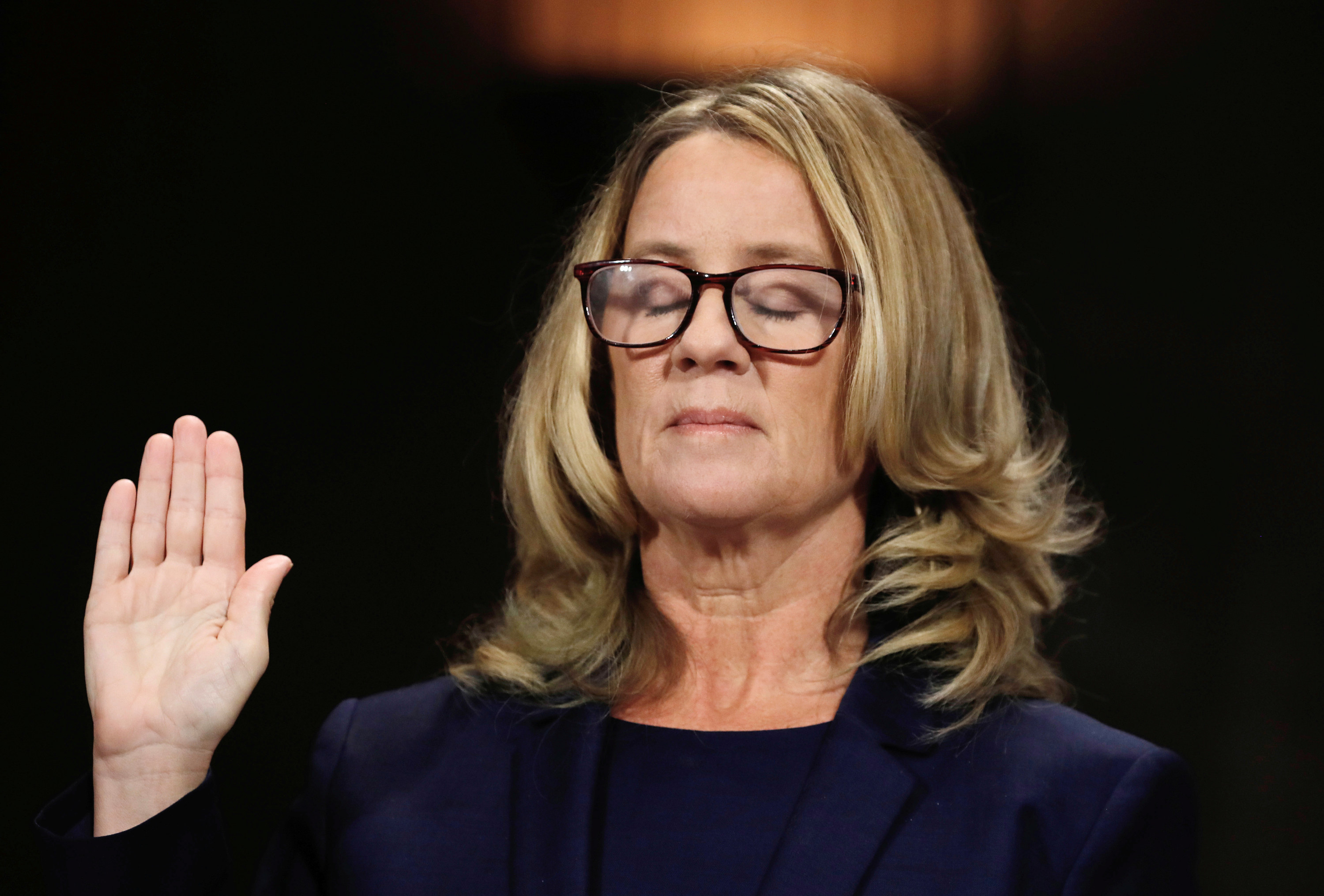
Carefully contained anger has a role to play in history. Over the years, we’ve watched Anita Hill testifying against Clarence Thomas to an all-male, all-white jury that dismissed her account of being harassed at work. We read the letter that Chanel Miller read out to Brock Turner — a man who sexually assaulted her, but served only three months in prison. We witnessed Christine Blasey Ford’s restrained terror when she was forced to face the man who she said sexually assaulted her. We listened to Nadia Murad, as she described with every shred of dignity she could muster the ethnic cleansing, genocide, and rape of Yazidis — and then again, when Yazidi women were made to confront their rapists on the news.
It is telling that the backlash against the #MeToo movement, in the form of defamation and libel and aggressive defense lawyers, has sought to drag women back to the courtroom: a space they did not trust with the trauma of their abuse in the first place, a place where they are treated as though they cannot be credible witnesses to their own truths.
Yet women’s rage is still unruly: It frustrates all attempts to contain it, shocks, confuses, and provokes. And its unruliness is productive. What else can explain the fact that women are still gathering and marching together across the world? That a day after Donald Trump — a man who was recorded on tape bragging about sexually assaulting women — was confirmed as president of the USA, women held the largest protest in American history? This year, women declared a feminist emergency across 250 cities and towns in Spain, after years of gang rape acquittals, domestic violence, and murders, despite being called “psychopathic feminazis.” In Argentina, the murder of teenage girls, abortion rights, and widespread harassment sparked #NiUnaMenos (Not One Less Woman, Not One More Death) — mass strikes in 2015 which spread across Peru, Bolivia, Uruguay, and El Salvador, and most recently Chile, where this year, a street protest has turned into a feminist anthem performed across Istanbul and Latin America. In South Korea, over 40,000 women protested an epidemic of spy cameras in dressing rooms, unleashing the largest women-only strike in the country’s history. And in India, women came together to form a 385-mile-long human wall against hundreds of years of patriarchy that illegally restricts their entry into a Hindu temple.
It’s 2019, and everything is both terrible and fine. If you feel tired, inhale, exhale, drink some water, and take a break. But remember, even this form of self-care is a luxury for 785 million people on this planet who lack access to clean water, and hours spent looking for water locks women across the world in a cycle of poverty and abuse. In China, polluted air is being linked to an increased risk of miscarriages; in India, Pakistan, Sydney, and California, a deep breath can be hazardous.
Meanwhile, that thing we all need more of — time — is marching on, and so must we. ●